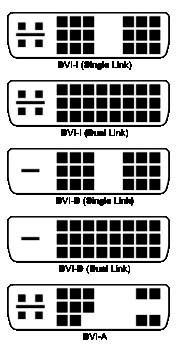
DVI Single Link and DVI Dual Link refer to the amount of pins, and thus the amount of bandwidth, that a DVI cable can use. DVI Single Link has enough bandwidth to carry 1920x1080 @ 60hz signal, and up to 3,840 × 2,400 @ 17hz. DVI Dual Link can carry 1,920 × 1,080 @ 85hz, up to 3,840 × 2,400 @ 33hz. Figure 1 shows what each type of connector looks like in both DVI-I and DVI-D configurations.
DVI-I and DVI-D refer to the extra 4 pins in a square pattern on the DVI connector. DVI-I (and DVI-A) carry those pins, and allows an adaptor to convert the signal from DVI to the older analog VGA standard. This option is not available on DVI-D ports, as they do not have the appropriate configuration. Figure 1 shows what each of these connectors look like in both their single and dual link configurations.
Figure 1: The different configurations for DVI ports and cables (source: Wikipedia)
If you require more technical information, please see the Wikipedia article, located here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Visual_Interface.