|
Because this new dual voltage standard is still fairly new, we have included some detailed information about the AGP 2.0 voltage requirements, taken from pages 155 and 156 of the AGP 2.0 Specifications Handbook (4 May 1998, Intel Corporation): |
|
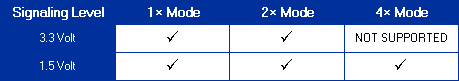
| The A.G.P. interface allows signaling at either 3.3 volts or 1.5 volts. The signaling level is determined through the value of Vddq I/O interface voltage. A.G.P. add-in cards operate at one of the two signaling levels and can only be plugged into a motherboard capable of supporting that particular signaling level. The signaling level of the motherboard is indicated by the position of the key in the A.G.P connector. In the case of the universal connector where no key exists, the TYPEDET# pin on the add-in card indicates to the platform the signaling level for that card. Only core logic devices that support the universal connector need to have interfaces capable of operating a either value of Vddq. All other core logic and all graphics devices operate at just one value of Vddq. Note that the interface signaling level is determined by the level of Vddq independent of transfer rate or whether the interface protocol is PCI or A.G.P. The included Table shows the allowed signaling levels for each data transfer mode. The 1x and 2x modes can operate at either signaling level. The 4x mode is restricted to the 1.5 volt signaling level because of signal integrity limitations. As mentioned above, signaling level is determined by the connector on the motherboard or by the TYPEDET# signal on universal connectors. The signaling rate is determined by software negotiation based on the capabilities of the A.G.P. master and target. | |
 |
Article Viewed: times since
 The
the introduction of newer motherboards that support the AGP 2.0 Specification,
there have been quite a few questions as to which cards of ours will support a
motherboard that only provides 1.5 volts to the AGP slot. The answer is very simple:
all of our AGP cards are based on the AGP 2.0 Specification, which allows for
operation in 1.5 volt of 3.3 volt configuration. This means that all of our cards
will operate in a 1.5 volt configuration.
The
the introduction of newer motherboards that support the AGP 2.0 Specification,
there have been quite a few questions as to which cards of ours will support a
motherboard that only provides 1.5 volts to the AGP slot. The answer is very simple:
all of our AGP cards are based on the AGP 2.0 Specification, which allows for
operation in 1.5 volt of 3.3 volt configuration. This means that all of our cards
will operate in a 1.5 volt configuration.