|
Differences In Memory Mean Differences In Performance You may be wondering, why some video cards are offered at a much lower price than other than the same video card manufactured elsewhere. Could it be the bundled software, special GPU cooling unit or even the nicely designed box? It’s possible. However, there is another way to lower the cost of a video card without the end-user even knowing it. This is achieved by implementing slower and cheaper video memory on the video card, which does not meet the original NVIDIA reference design of that particular video card. Because there are so many possible variations, you need to pay close attention to what you are buying. Sometimes saving $5 can cut your performance in half. EVGA.com believes that everyone should be able to know exactly what they're buying and get exactly what they pay for. So take a look at these graphs and see how memory variations play a huge role in video card performance.
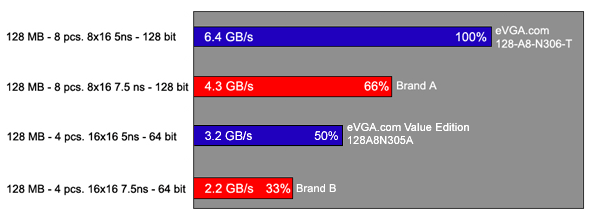
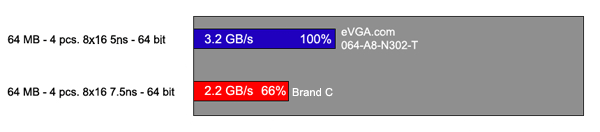
As you can see from these GeForce FX 5200 benchmark graphs, different memory variations on the same video card shows drastic differences in benchmark results. In short, BANDWIDTH COUNTS! The 3 most important factors to understanding your card's memory configuration are: the memory access time, its maximum operating speed in MHz, and the memory bus width. Determining The Memory Access Time When you take a close look at the memory of a video card, you will see the memory manufacturer’s name and the part number. The part number will look something like this: XXXXXXXXXX-X. The number after the dash (-) normally determines the memory access time in nanoseconds (ns). For example, take a look at the picture below:
Determining Maximum Operating Speed in MHz To determine the true Video Memory MHz, we must find out the Video Memory’s speed. By using the example from above, we found that the memory’s speed is rated at 5ns. We then use a simple formula that will allow us to determine the true Video Memory MHz. 1 divided by the Memory Access Time = Memory Speed in MHz By using the example above, we divide 1 by 5ns, which is the memory speed and we get: 1 / 5ns = 200MHz If the memory above is an SDR memory, then it should run at 200MHz stably. If the memory above is DDR (Double Data Rate), then we multiply 200MHz by 2 and get 400MHz, which is the MHz speed the memory can handle up to without a problem. Determining The Memory Bus Width This portion of the guide is probably the most crucial element in determining a video card’s performance. There are two ways to determine the bit bus of a video card’s memory. One way is to use a formula to calculate the bit bus. The second way is much simpler, by looking at the number of memory pieces. Majority of the video cards out in the market have either 8 or 4 pieces of memory on the video card. 8 pieces of
memory normally operates at 128-bit bus Here is a good example differentiating the performance of 32, 64 and 128-bit bus of memory: Let’s say there are three highways, all perfectly parallel to each other. Imagine Highway 1 (128-bit) as a 4 lane highway, Highway 2 (64-bit) as a 2 lane highway and Highway 3 (32-bit) as a 1 lane highway. If all cars were driving home from Point A to Point B, including yourself, on all three highways, you would get home faster on Highway 1 because of the wider width of having 4 lanes. Highway 3 would have more traffic than Highway 1, due to its 1 lane and can cause you to get home slower. So, with this information in mind, you can safely try and determine your card's memory configuration. Once you do, just compare it to the graphs found earlier in this artice and you can see how your card stacks up against others in the market. Special Memory Warning: Mix-Matching Video Memory This is
a touchy subject, so we will be explain this very briefly. There are a few
video cards floating around in this market that have been implemented with
different brands and speeds of the memory (ns). Theoretically, this should
be able to work. However, there have been reports of computer systems crashing
and locking up with this type of video memory configuration. One way to
tell if your video card has the same memory pieces is to take a look at
the memory and make sure the Manufacturer and Part Numbers are all the same.
Also, you can do a search online and check the memory part number on the
Memory Manufacturer’s website.
Article Viewed: times since
|
 Original
Memory Specs VS Other Variations
Original
Memory Specs VS Other Variations